SimpleCxxLib packageclass GObjectGObject
itself is an abstract class, which means that you are not
allowed to construct a GObject directly but must instead
construct one of the concrete subclasses.
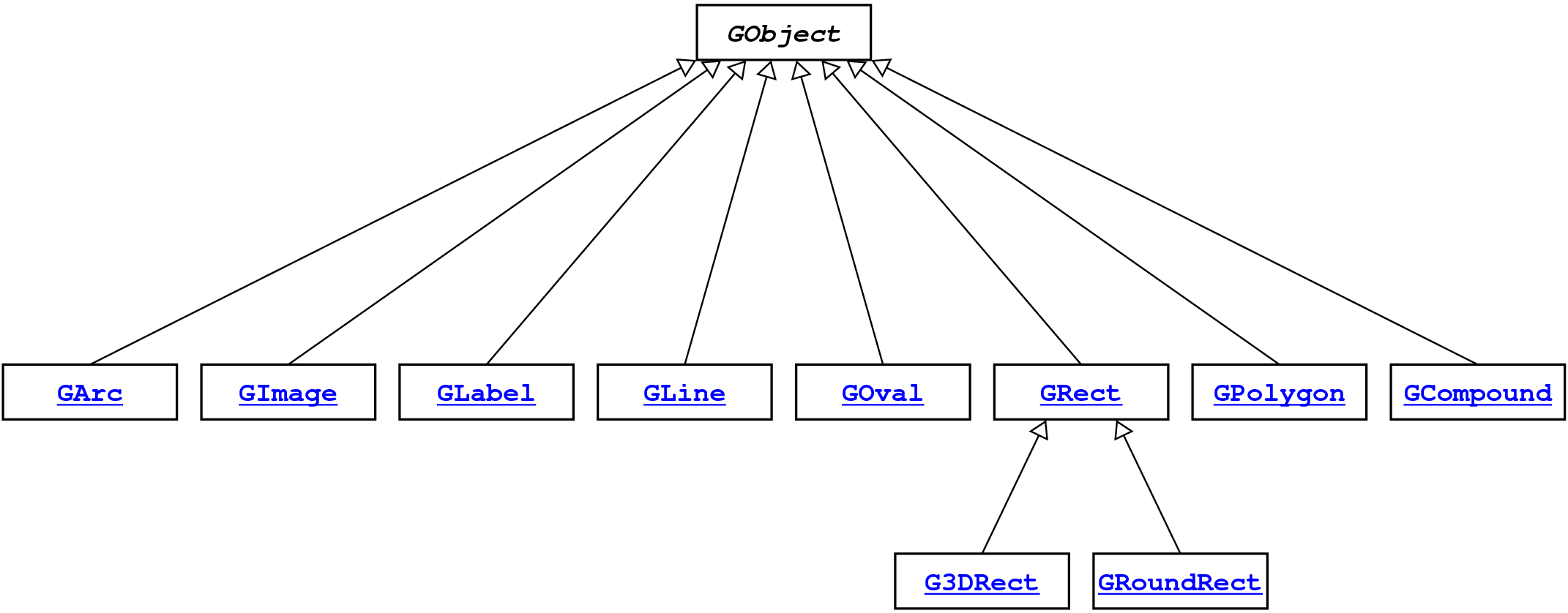
These subclasses form a hierarchy that looks like this:

Most methods used for graphics take a pointer to a GObject
rather than the GObject itself. Applications that use
GObject pointers therefore use the arrow operator
(->) to apply methods to the object pointer.
For examples illustrating the use of the GObject class, see
the descriptions of the individual subclasses.
| Methods | |
contains(x, y) | Returns true if the specified point is inside the object. |
| Returns the bounding box of this object, which is defined to be the smallest rectangle that covers everything drawn by the figure. | |
| Returns the color used to display this object. | |
| Returns the height of this object, which is defined to be the height of the bounding box. | |
| Returns the width of the line used to draw this object. | |
Returns the location of this object as a GPoint. | |
Returns a pointer to the GCompound that contains this object. | |
Returns the size of the object as a GDimension. | |
Returns the concrete type of the object as a string, as in "GOval" or "GRect". | |
| Returns the width of this object, which is defined to be the width of the bounding box. | |
| Returns the x-coordinate of the object. | |
| Returns the y-coordinate of the object. | |
Returns true if this object is visible. | |
Moves the object on the screen using the displacements dx and dy. | |
Transforms the object by rotating it theta degrees counterclockwise around its origin. | |
scale(sx, sy) | Scales the object by the specified scale factors. |
| Moves this object one step toward the back in the z dimension. | |
| Moves this object one step toward the front in the z dimension. | |
| Moves this object to the back of the display in the z dimension. | |
| Moves this object to the front of the display in the z dimension. | |
| Sets the color used to display this object. | |
| Sets the width of the line used to draw this object. | |
setLocation(x, y) | Sets the location of this object to the specified point. |
| Sets whether this object is visible. | |
| Returns a printable representation of the object. | |
double getX() const;
Usage:
double x = gobj->getX();
double getY() const;
Usage:
double y = gobj->getY();
GPoint getLocation() const;
GPoint.
Usage:
GPoint pt = gobj->getLocation();
void setLocation(const GPoint & pt); void setLocation(double x, double y);
Usage:
gobj->setLocation(pt); gobj->setLocation(x, y);
void move(double dx, double dy);
dx and dy.
Usage:
gobj->move(dx, dy);
double getWidth() const;
Usage:
double width = gobj->getWidth();
double getHeight() const;
Usage:
double height = gobj->getHeight();
GDimension getSize() const;
GDimension.
Usage:
GDimension size = gobj->getSize();
GRectangle getBounds() const;
getLocation. Given a GLabel
object, for example, getLocation returns the coordinates
of the point on the baseline at which the string begins; the
getBounds method, by contrast, returns a rectangle that
covers the entire window area occupied by the string.
Usage:
GRectangle rect = gobj->getBounds();
void setLineWidth(double lineWidth);
Usage:
gobj->setLineWidth(lineWidth);
double getLineWidth() const;
Usage:
double lineWidth = gobj->getLineWidth();
void setColor(string color); void setColor(int rgb);
color
string is usually one of the predefined color names:
BLACK,
BLUE,
CYAN,
DARK_GRAY,
GRAY,
GREEN,
LIGHT_GRAY,
MAGENTA,
ORANGE,
PINK,
RED,
WHITE, and
YELLOW.
The case of the individual letters in the color name is ignored, as
are spaces and underscores, so that the color DARK_GRAY
can be written as "Dark Gray".
The color can also be specified as a string in the form
"#rrggbb" where rr, gg, and
bb are pairs of hexadecimal digits indicating the
red, green, and blue components of the color, respectively.
Usage:
gobj->setColor(color);
string getColor() const;
"#rrggbb",
where rr, gg, and bb are
the red, green, and blue components of the color, expressed as
two-digit hexadecimal values.
Usage:
string color = gobj->getColor();
void scale(double sf); void scale(double sx, double sy);
sf in both
dimensions, so that invoking gobj->scale(2) doubles the
size of the object. The second form applies independent scale factors
to the x and y dimensions.
Usage:
gobj->scale(sf); gobj->scale(sx, sy);
void rotate(double theta);
theta degrees
counterclockwise around its origin.
Usage:
gobj->rotate(theta);
void setVisible(bool flag);
Usage:
gobj->setVisible(flag);
bool isVisible() const;
true if this object is visible.
Usage:
if (gobj->isVisible()) ...
void sendForward();
Usage:
gobj->sendForward();
void sendToFront();
Usage:
gobj->sendToFront();
void sendBackward();
Usage:
gobj->sendBackward();
void sendToBack();
Usage:
gobj->sendToBack();
bool contains(GPoint pt) const; bool contains(double x, double y) const;
true if the specified point is inside the object.
Usage:
if (gobj->contains(pt)) ... if (gobj->contains(x, y)) ...
string getType() const;
"GOval" or "GRect".
Usage:
string type = gobj->getType();
string toString() const;
Usage:
gobj->toString();
GCompound *getParent() const;
GCompound that contains this
object. Every GWindow is initialized to contain a single
GCompound that is aligned with the window. Adding
objects to the window adds them to that GCompound,
which means that every object you add to the window has a parent.
Calling getParent on the top-level GCompound
returns NULL.
Usage:
GCompound *parent = gobj->getParent();