SimpleCxxLib packageclass GArc : public GObjectx,
y, width, height)
start)
sweep)
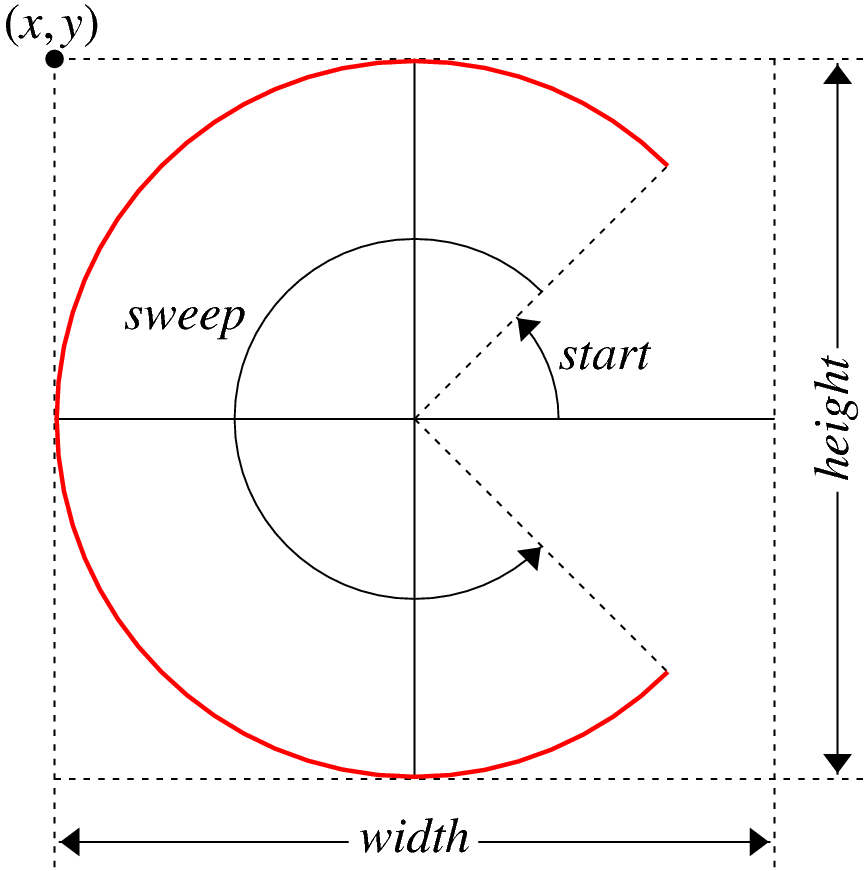
All angles in a GArc description are measured in
degrees moving counterclockwise from the +x axis. Negative
values for either start or sweep indicate
motion in a clockwise direction.
The following diagram illustrates the interpretation of these parameters for the arc shown in red:

| Constructor | |
GArc(x, y, width, height, start, sweep) | Creates a new GArc object consisting of an elliptical arc. |
| Methods | |
| Returns the point at which the arc ends. | |
| Returns the color used to display the filled region of this arc. | |
| Returns the boundaries of the rectangle used to frame the arc. | |
Returns the starting angle for this GArc object. | |
| Returns the point at which the arc starts. | |
Returns the sweep angle for this GArc object. | |
Returns true if the arc is filled. | |
| Sets the color used to display the filled region of this arc. | |
Sets the fill status for the arc, where false is outlined and true is filled. | |
setFrameRectangle(x, y, width, height) | Changes the boundaries of the rectangle used to frame the arc. |
Sets the starting angle for this GArc object. | |
Sets the sweep angle for this GArc object. | |
GArc(double width, double height, double start, double sweep); GArc(double x, double y, double width, double height, double start, double sweep);
GArc object consisting of an elliptical arc.
The first form creates a GArc whose origin is the point
(0, 0); the second form positions the GArc at the
point (x, y).
The following screenshots show several examples of how the
GArc constructor interprets the start
and sweep parameters:
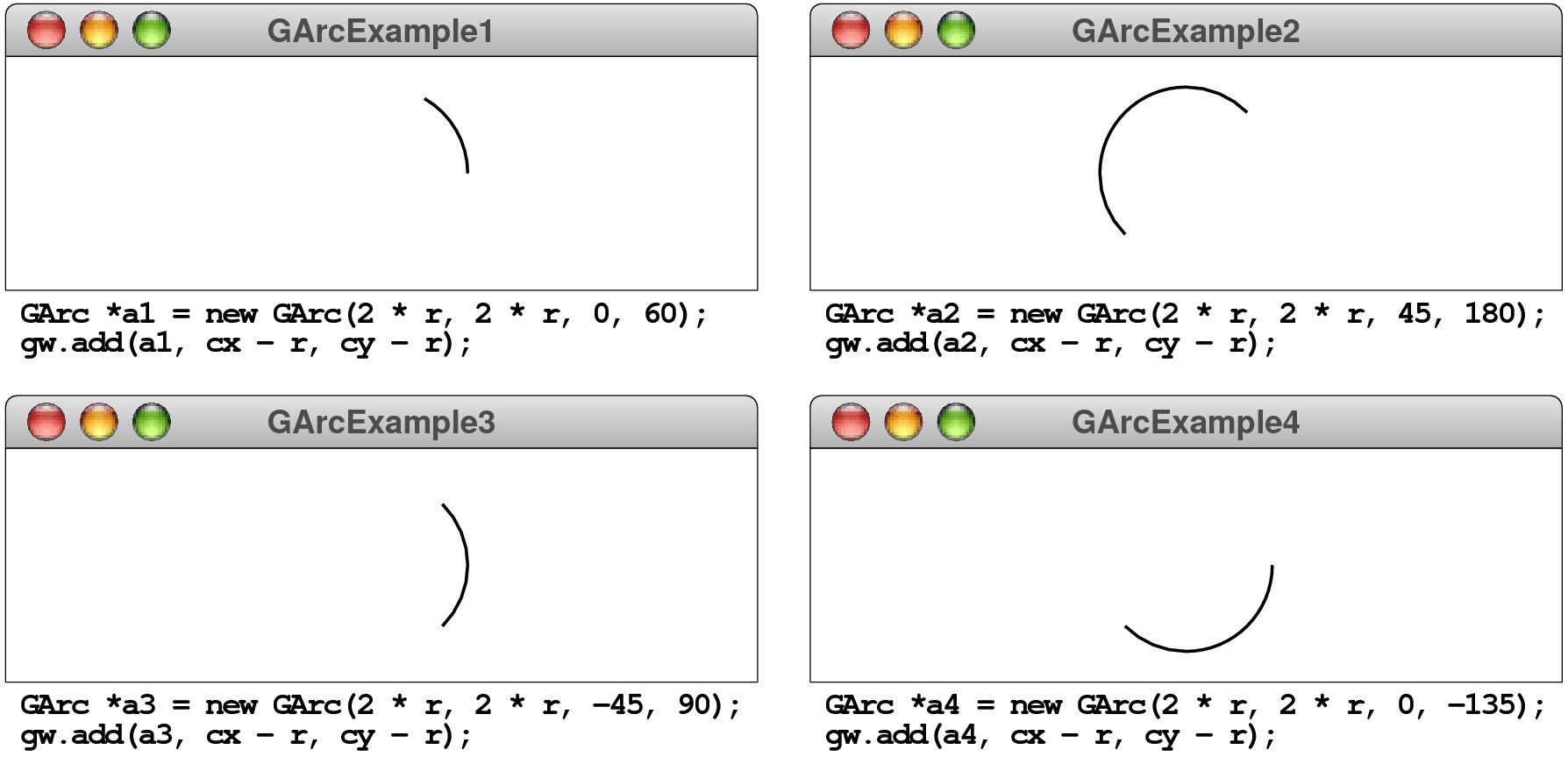
In the code fragments underneath each of these diagrams, r
is the radius of the circular arc, and cx and cy
are the coordinates of the center or the window.
Usage:
GArc *arc = new GArc(width, height, start, sweep); GArc *arc = new GArc(x, y, width, height, start, sweep);
void setStartAngle(double start);
GArc object.
Usage:
arc->setStartAngle(start);
double getStartAngle() const;
GArc object.
Usage:
double angle = arc->getStartAngle();
void setSweepAngle(double start);
GArc object.
Usage:
arc->setSweepAngle(start);
double getSweepAngle() const;
GArc object.
Usage:
double angle = arc->getSweepAngle();
GPoint getStartPoint() const;
Usage:
GPoint pt = arc->getStartPoint();
GPoint getEndPoint() const;
Usage:
GPoint pt = arc->getEndPoint();
void setFrameRectangle(const GRectangle & rect); void setFrameRectangle(double x, double y, double width, double height);
Usage:
arc->setFrameRectangle(rect); arc->setFrameRectangle(x, y, width, height);
GRectangle getFrameRectangle() const;
Usage:
GRectangle rect = arc->getFrameRectangle();
void setFilled(bool flag);
false is
outlined and true is filled. If a GArc is
unfilled, the figure consists only of the arc itself. If a
GArc is filled, the figure consists of the
pie-shaped wedge formed by connecting the endpoints of the arc to
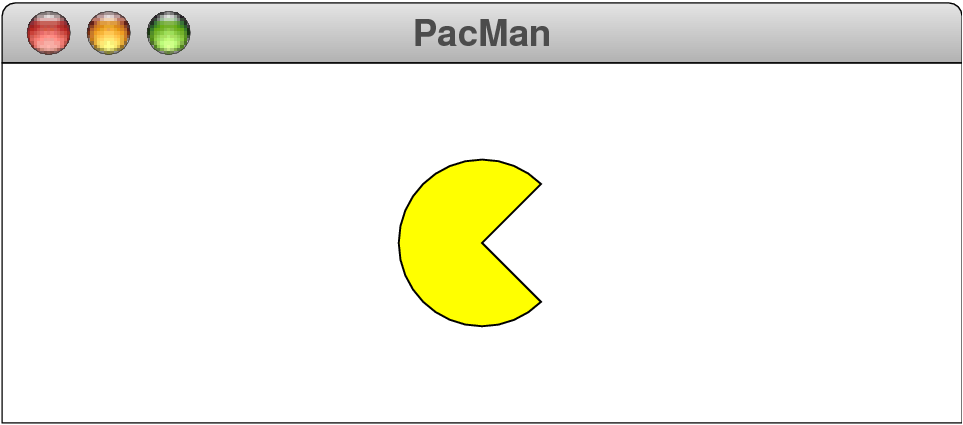
the center. As an example, the following program draws a 270-degree
arc starting at 45 degrees, filled in yellow, much like the character
in the PacMan video game:
int main() {
GWindow gw;
cout << "This program draws the PacMan character." << endl;
double cx = gw.getWidth() / 2;
double cy = gw.getHeight() / 2;
double r = 25;
GArc *pacman = new GArc(cx - r, cy - r, 2 * r, 2 * r, 45, 270);
pacman->setFilled(true);
pacman->setFillColor("YELLOW");
gw.add(pacman);
return 0;
}
The program results in the following picture:
Usage:
arc->setFilled(flag);
bool isFilled() const;
true if the arc is filled.
Usage:
if (arc->isFilled()) ...
void setFillColor(string color); void setFillColor(int rgb);
setColor
method.
Usage:
arc->setFillColor(color);
string getFillColor() const;
getFillColor returns the empty string.
Usage:
string color = arc->getFillColor();